biotite.sequence.Annotation¶
- class biotite.sequence.Annotation(features=None)[source]¶
Bases:
CopyableAn
Annotationis a set of features belonging to one sequence.Its advantage over a simple list is the base/residue position based indexing: When using slice indices in Annotation objects, a subannotation is created, containing copies of all
Featureobjects whose first and last base/residue are in range of the slice. If the slice starts after the first base/residue or/and the slice ends before the last residue, the position out of range is set to the boundaries of the slice (theFeatureis truncated). In this case theFeatureobtains theLocation.Defect.MISS_LEFTand/orLocation.Defect.MISS_RIGHTdefect. The third case occurs when aFeaturestarts after the slice ends or aFeatureends before the slice starts. In this case theFeaturewill not appear in the subannotation.The start or stop position in the slice indices can be omitted, then the subannotation will include all features from the start or up to the stop, respectively. Step values are ignored. The stop values are still exclusive, i.e. the subannotation will contain a not truncated
Featureonly if its last base/residue is smaller than the stop value of the slice.Integers or other index types are not supported. If you want to obtain the
Featureinstances from theAnnotationyou need to iterate over it. The iteration has no defined order. Alternatively, you can obtain a copy of the internalFeatureset viaget_features().Multiple
Annotationobjects can be concatenated to oneAnnotationobject using the ‘+’ operator. SingleFeatureinstances can be added this way, too. If a feature is present in bothAnnotationobjects, the resultingAnnotationwill contain this feature twice.- Parameters
- featuresiterable object of Feature, optional
The features to create the
Annotationfrom. if not provided, an emptyAnnotationis created.
Examples
Creating an annotation from a feature list:
>>> feature1 = Feature("CDS", [Location(-10, 30 )], qual={"gene" : "test1"}) >>> feature2 = Feature("CDS", [Location(20, 50 )], qual={"gene" : "test2"}) >>> annotation = Annotation([feature1, feature2]) >>> for f in sorted(list(annotation)): ... print(f.qual["gene"], "".join([str(loc) for loc in f.locs])) test1 -10-30 > test2 20-50 >
Merging two annotations and a feature:
>>> feature3 = Feature("CDS", [Location(100, 130 )], qual={"gene" : "test3"}) >>> feature4 = Feature("CDS", [Location(150, 250 )], qual={"gene" : "test4"}) >>> annotation2 = Annotation([feature3, feature4]) >>> feature5 = Feature("CDS", [Location(-50, 200 )], qual={"gene" : "test5"}) >>> annotation = annotation + annotation2 + feature5 >>> for f in sorted(list(annotation)): ... print(f.qual["gene"], "".join([str(loc) for loc in f.locs])) test5 -50-200 > test1 -10-30 > test2 20-50 > test3 100-130 > test4 150-250 >
Location based indexing, note the defects:
>>> annotation = annotation[40:150] >>> for f in sorted(list(annotation)): ... gene = f.qual["gene"] ... loc_str = "".join([f"{loc} {loc.defect}" for loc in f.locs]) ... print(gene, loc_str) test5 40-149 > Defect.MISS_RIGHT|MISS_LEFT test2 40-50 > Defect.MISS_LEFT test3 100-130 > Defect.NONE
- add_feature(feature)¶
Add a feature to the annotation.
- Parameters
- featureFeature
Feature to be added.
- copy()¶
Create a deep copy of this object.
- Returns
- copy
A copy of this object.
- del_feature(feature)¶
Delete a feature from the annotation.
- Parameters
- featureFeature
Feature to be removed.
- Raises
- KeyError
If the feature is not in the annotation
- get_features()¶
Get a copy of the internal feature set.
- Returns
- feature_listlist of Feature
A copy of the internal feature set.
- get_location_range()¶
Get the range of feature locations, i.e. the first and exclusive last base/residue.
- Returns
- intstart
Start location.
- intstop
Exclusive stop location.
Gallery¶

Genome comparison between chloroplasts and cyanobacteria
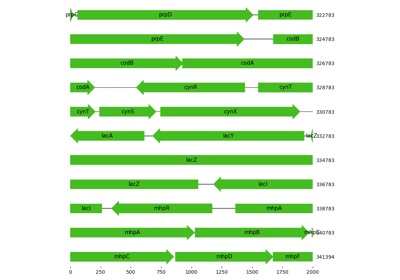
Visualization of region in proximity to lac operon

Three ways to get the secondary structure of a protein







